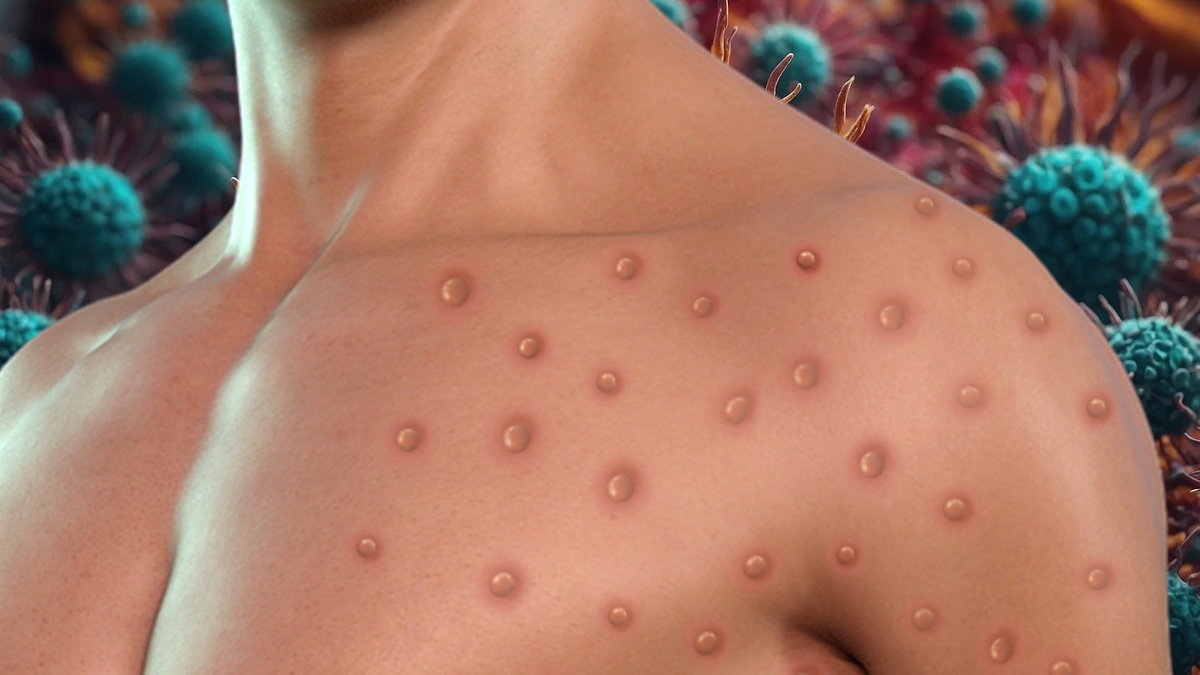
The World Health Organization (WHO) took action and declared a global public health emergency after the monkeypox virus spread from the Democratic Republic of Congo to other countries. Alright, What is Monkeypox virus?
After COVID-19, which emerged in Wuhan, China in November 2019 and reached a mortality rate of 3.4% worldwide as of 2020, the world faced a new threat called Monkeypox.
In this guide monkeypox symptoms We will answer many questions about the new virus, including:
Monkeypox was first seen in monkeys in a study conducted on laboratory animals in Copenhagen, Denmark, in 1958. For this reason, the disease was called monkeypox.
Monkeypox is the disease caused by monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family. This virus, also known as Mpox, is among the zoonotic diseases.
Symptoms of this disease usually last 2 to 4 weeks. In addition to mild symptoms, severe cases may also occur. Monkeypox can even cause people to lose their lives. The disease was first seen in humans in 1970 in a 9-year-old child in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Since 1970, monkeypox disease has been detected in 11 African countries: Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Nigeria, Republic of Congo, Sierra Leone and South Sudan.
Between 1970 and 1980, 59 people contracted monkeypox. Since 2017, more than 500 suspected cases and more than 200 confirmed cases have been observed in Nigeria.
According to the report shared by Africa CDC on August 9, 2024, 2,822 people caught monkeypox in 13 African countries from January to August 8. The number of suspected cases was announced as 14,719. 517 people died due to this disease, 511 of whom were in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said, “It is clear that a coordinated international response is essential to stop these epidemics and save lives.”
There is more than one way for monkeypox disease to be transmitted from person to person. Close contact such as hugging, sexual intercourse and massage cause the disease to be transmitted.
Close contact with items such as clothing, bed linen and towels that have been in contact with infected people can also lead to the transmission of the disease. This disease is also transmitted by rodents such as mice and squirrels.
The first symptoms of the disease can appear between 5 and 21 days after infection. According to the information shared, there is currently no specific treatment method for this virus. This disease is treated with antiviral drugs.
Most of the cases are mild, but in some cases it can be fatal. From the beginning of 2024 to August 8, 2,822 people in 13 African countries contracted monkeypox.
The number of suspected cases was announced as 14,719. 517 people died due to this disease, 511 of whom were in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
According to the information provided, there are currently two different species of monkey flower: Clade 1 and Clade 1b. Clade 1 is an endemic species in Central Africa, while Clade 1b is a more severe species compared to the other.
Monkeypox virus was first seen in humans in 1970 in a 9-year-old child in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Research for the most talked about disease of recent days, X, has accelerated. WHO is on alert. So, what is disease X? Let’s look at the details together!
What do you think about monkeypox? Don’t forget to share your thoughts on the subject with us in the comments section below.
Source link: https://www.tamindir.com/blog/maymun-cicegi-virusu-nedir_89927/
Web sitemizde ziyaretçilerimize daha iyi hizmet sağlayabilmek adına bazı çerezler kullanıyoruz. Web sitemizi kullanmaya devam ederseniz çerezleri kabul etmiş sayılırsınız.
Gizlilik Politikası